XML REPORTING SOFTWARE FOR COUNTRY BY COUNTRY REPORTING (CBC)

XML Reporting software for COUNTRY BY COUNTRY REPORTING (CbCR).
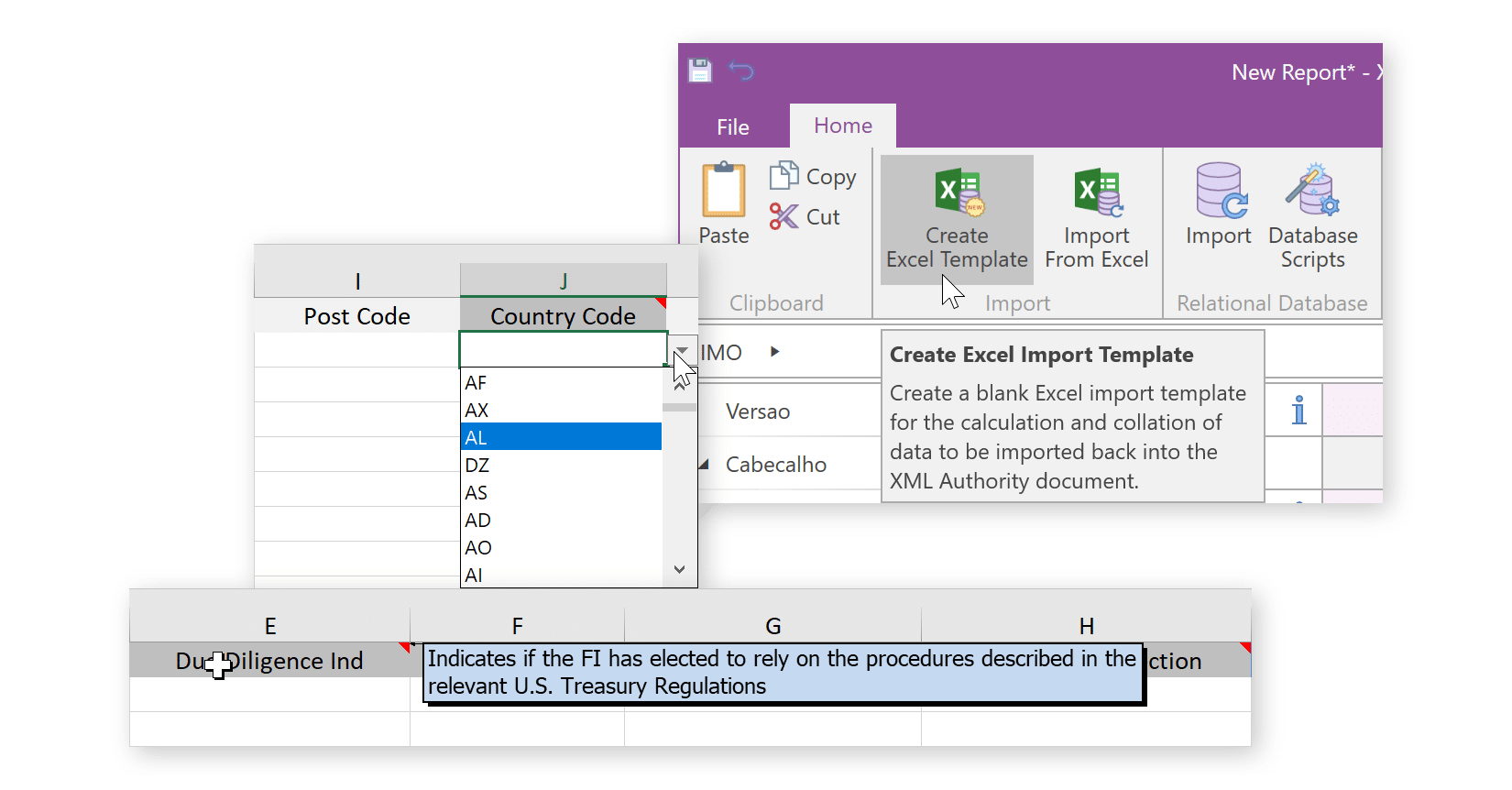
Connect directly to data in Microsoft Excel or Relational Databases (SQL).
Introducing XML Authority.
Learn how XML Authority can help you simplify and streamline your XML reporting.
HOW DOES IT WORK?
2. Create your reporting template
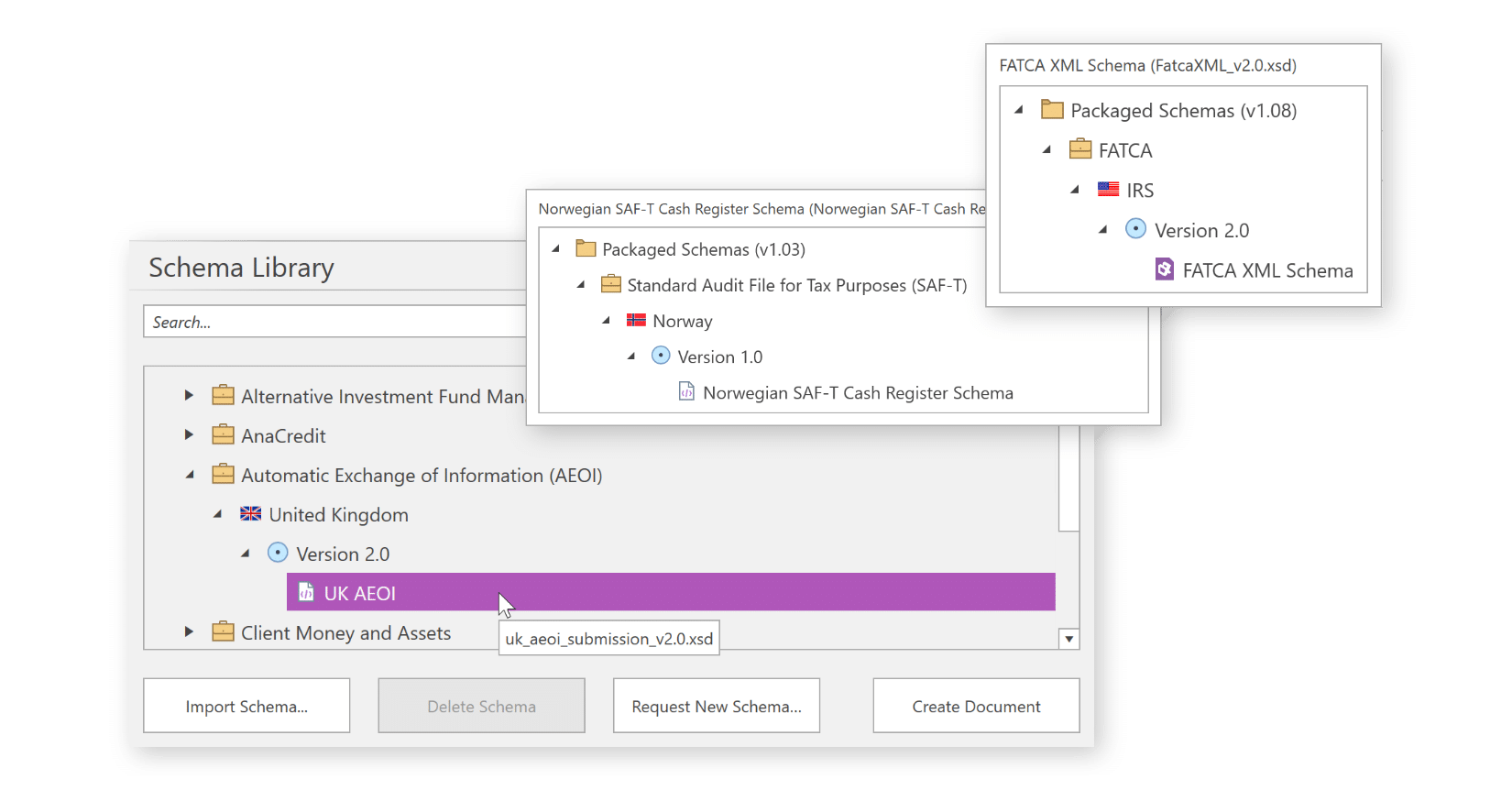
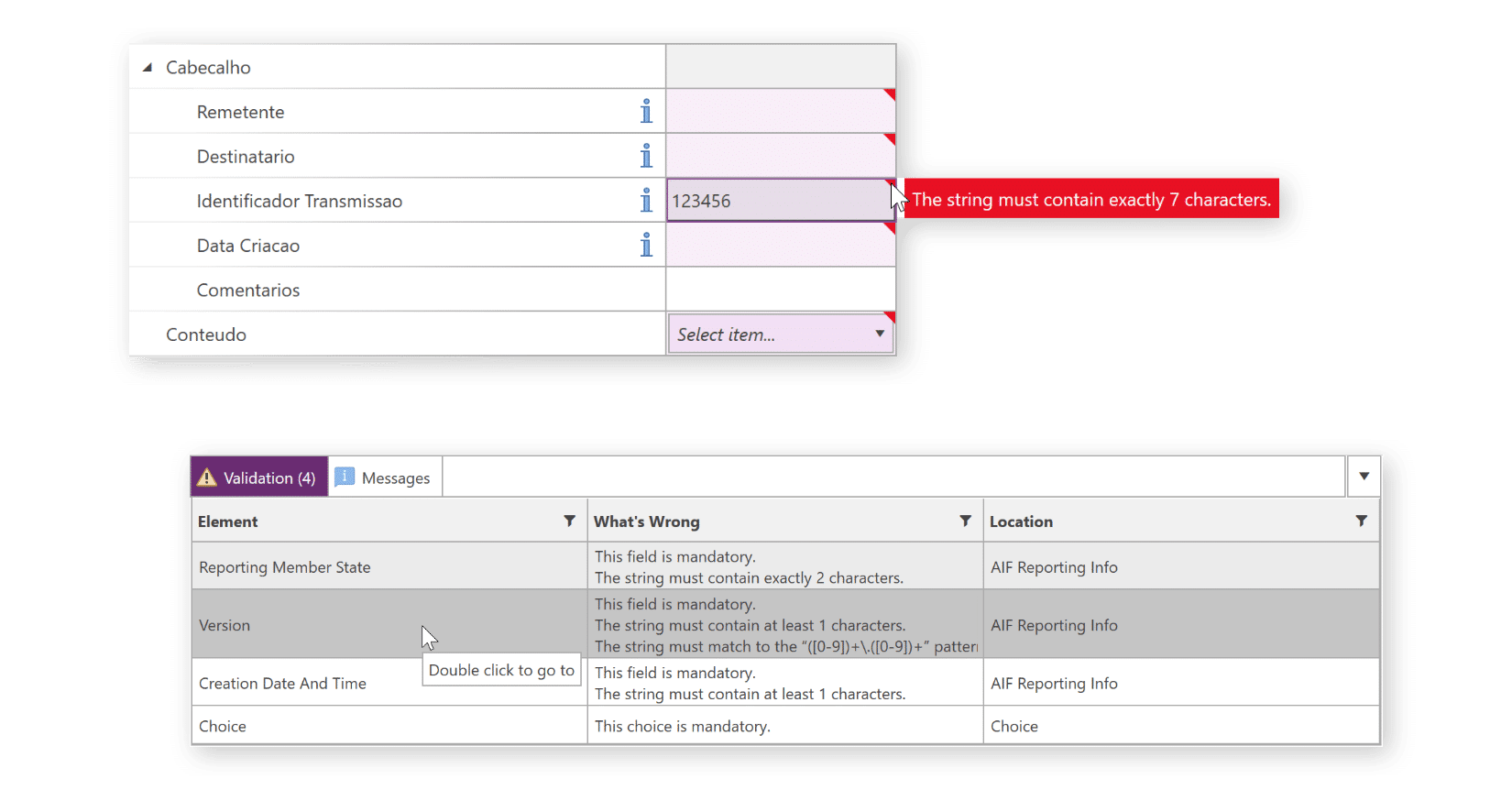
Schemas are presented as easy to interpret forms and tables. Mandatory fields are highlighted and guidance is available throughout the schema.
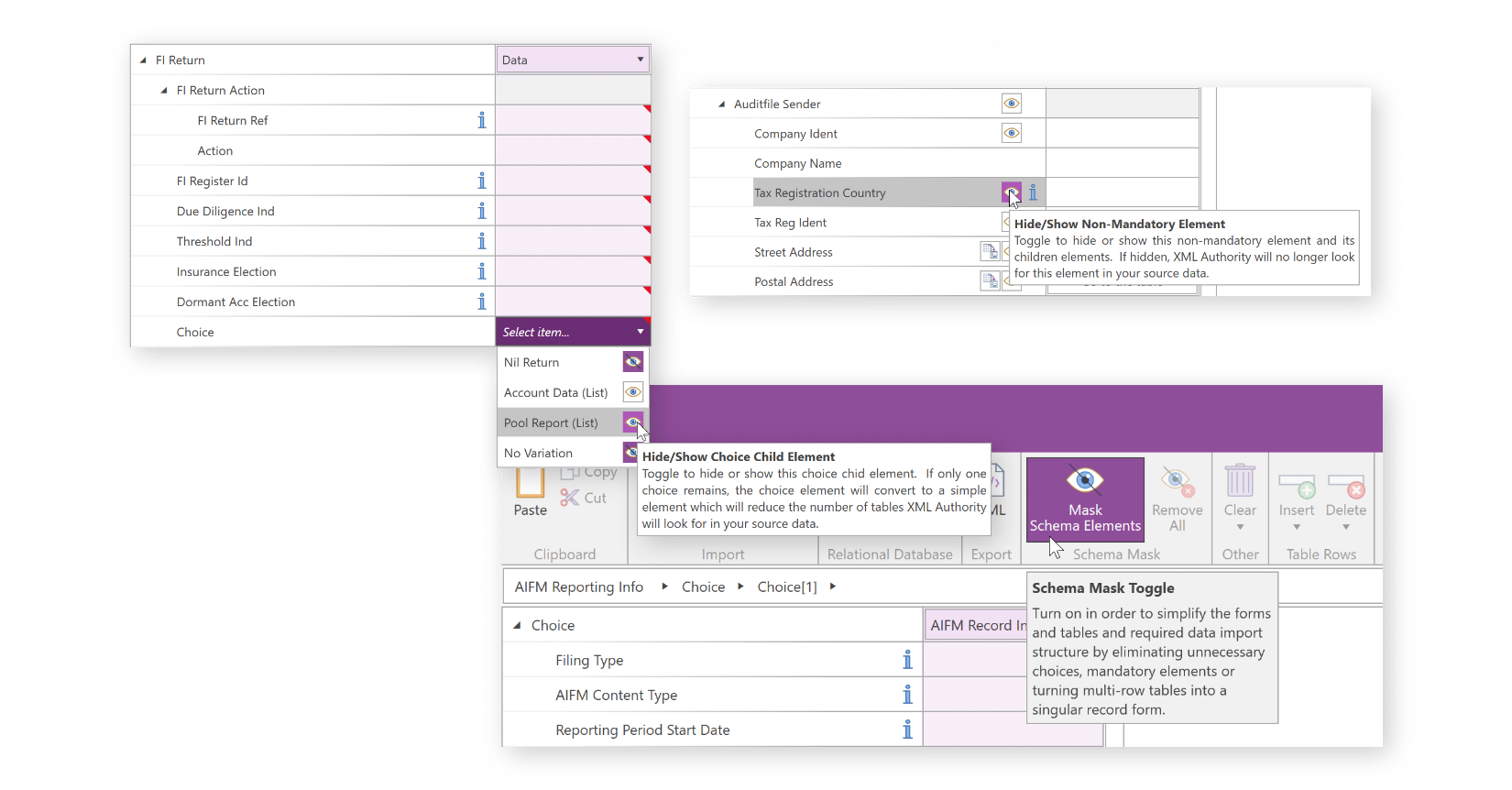
You can modify the structure of the schema and remove non-mandatory fields to match the structure of your data and create a reporting template to be used across reporting periods.
4. Validate to ensure acceptance of submission
XML Authority’s interactive validation messages direct you right to the cause of any data issues that could cause the rejection of a submission.
REQUEST A DEMO:
- Seeing the software operate is the best way to understand how it works.
- We can answer any questions for your specific requirements.
- Together we can assess how our solution will work for you.
- ESMA ESEF
- UK HMRC
- Irish Revenue
- Danish Business Authority
- and many others
- EBA CRD V (COREP & FINREP)
- EIOPA Solvency II
- Single Resolution Board
- National Banking and Insurance
XBRL Reporting
XML AUTHORITY FEATURES
Create XML files for submission to regulators. XML Authority simplifies this process by providing a human-readable view of the data requirements as a set of annotated forms and tables.
Validate to ensure compliance with data requirements. Easily validate and resolve issues using XML Authority’s interactive validation messages designed to take you right to the cause of any data quality issues.